What is Business Analytics?
Business analytics (BA) is the process of evaluating data in order to gauge business performance and to extract insights that may facilitate strategic planning. It aims to identify the factors that directly impact business performance, such as ie. revenue, user engagement, and technical availability.
BA takes data from all business levels, from product and marketing, to operations and finance. Where analytics at the IT layer has a more direct causal relationship, at the business layer metrics are interdependent and their behavior regularly fluctuates – making business analytics an especially complex process.
In this article we’ll explore how the integration of AI in business analytics is critical as the volume and complexity of data continues to grow, challenging traditional methods of data analysis using BI dashboards.
Why Business Analytics Matters?
Regardless of size or type, organizations need to collect and evaluate data to understand how their business performs. Critical decisions, such as changing pricing structures, or developing additional products and features, follow an understanding of the numbers and their financial impact.
According to Harvard Business School, 60 percent of businesses use BA to boost operational efficiency. For digital companies, this goes hand in hand with user experience. A smoothly functioning website or app is often a prerequisite for visitors agreeing to pay for goods.
The study also says 57 percent of businesses leverage BA to drive change and strategy, helping identify hidden opportunities and detecting performance gaps that would be hard to grasp on intuition alone. In 52 percent of businesses, BA facilitates monitoring revenue, although the metrics involved aren’t always limited to financial data. The concept is to collect data from all business units and analyze their impact on financial performance.
The Evolution of Data Analytics
Until late 1960, business analytics relied on handwritten or typed business reports, and people used some form of a calculator to carry out statistical ascertaining. The motivation was gaining visibility into the company’s activities and profitability by measuring, tracking, and recording quantifiable values, such as time and cost, and understanding how they relate.
Computers made this a lot easier. With the onset of SQL and relational databases, collecting and analyzing statistical data moved to the next level. It was still only the beginning of modern data analytics. Data warehouses and data mining allowed for more data to undergo statistical analysis. Companies started to use the ‘slice and dice’ technique in which they break down large data sets into smaller segments to get a deeper understanding of specific points of interest.
At this time, analysts still worked with historical data. Real-time data only entered the stage at the break of the millennium. When it became possible to analyze processes while they were happening, business analytics took on a much more significant role in digital business. Analytics could now be used as an operational tool and not merely as intelligence to back up strategies.
Once again, though, the amount of data became unmanageable. The need to collect data from various sources presented additional challenges. Big data was born and, together with cloud computing, enabled businesses to scale.
AI in Business Analytics
Not too long ago, agile, interactive dashboards were the business analyst’s dream come true. But for growing enterprises, data analysis needs are outgrowing the capabilities of KPI dashboards.
When the data analyst wants to investigate why a given anomaly occurs, they have to look at KPIs across data silos and manually identify relationships between them. Finding the root cause of an underlying issue can take a significant amount of time when analysts have to wade through dashboards as they work through a process of elimination.
Using AI in business analytics allows organizations to utilize machine learning algorithms to identify trends and extract insights from complex data sets across multiple sources. AI analytics probes deeper into data and correlates simultaneous anomalies, revealing critical insight into business operations.
Business analytics powered by AI can autonomously learn and adapt to changing behavioral patterns of metrics and is therefore significantly more precise in detecting anomalies and deviations. That means a significant reduction in false positives and meaningless alert storms and the surfacing of only the most business critical incidents.
Unlike traditional BI tools, by detecting business incidents in real-time and identifying the root cause, AI business analytics helps you remedy problems faster and capture opportunities sooner.
Benefits of Anodot’s AI-driven Business Analytics
Using AI in business analytics solutions like Anodot, autonomously learn the behavior of 100% of your data and correlates metrics in real-time. Anodot monitors all metrics at scale, enabling operators to achieve complete visibility over the total of services, processes, partners, customers, and business KPIs. Leveraging Anodot’s AI capabilities, you can significantly cut both TTD and TTR and protect your revenue streams from disruption.
Anodot’s autonomous monitoring platform learns the behavior patterns of all backend and frontend customer experience data and correlates between metrics to create context and visibility.
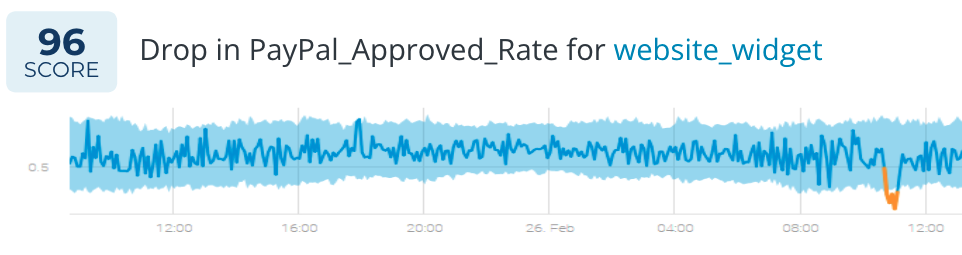
You can discover suspicious spikes or drops in engagement metrics or other user-experience-related parameters and act in real-time. In this example, an eCommerce customer was alerted to an unusual drop in approval rates for purchases paid for with PayPal.
Monitoring user experience also helps you identify opportunities to optimize and implement them in your business strategy. Anodot allows you to take your business analytics to the top level. Take the next step towards fully autonomous AI in business analytics monitoring.
Related Guides:
- Top 13 Cloud Cost Optimization: Best Practices for 2025
- Understanding FinOps: Principles, Tools, and Measuring Success
Related Products:
Ready to see our solution in action?
Prepare to see how Anodot leverages AI to constantly monitor and correlate business performance, identify revenue-critical issues, and provide real-time alerts and forecasts.