What Is FinOps?
FinOps is a cultural practice that brings financial accountability to the world of cloud computing. It’s a strategic approach that aids organizations in understanding their cloud costs and making informed business decisions.
FinOps is a new way of managing costs in an IT environment that is increasingly shifting towards the variable cost model of cloud services. It combines the best of the technical and financial worlds, resulting in an effective model for managing cloud costs. FinOps is all about collaboration and transparency, and its main goal is to maximize the value of your cloud investments.
It’s important to realize that FinOps does not exclusively focus on cost-cutting. It’s more about bringing clarity to your cloud expenditures, enabling you to make more strategic decisions. With FinOps, you can ensure that every dollar spent on the cloud is being put to good use.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about DevOps.
In this article:
- What is the FinOps Foundation?
- Why Is FinOps Adoption Growing? Key Benefits of FinOps
- The Three Pillars of FinOps
- The Principles of FinOps
- What Are FinOps Tools?
- Key Features of FinOps Tools
- KPIs for Measuring FinOps Success
- Best Practices to Implement a FinOps Program
What is the FinOps Foundation?
The FinOps Foundation is a non-profit trade association made up of FinOps experts and practitioners around the world. The goal of the Foundation is to promote best practices and standards for FinOps, facilitating knowledge sharing and professional development among its members.
The FinOps Foundation is playing an important role in the spread and maturation of the FinOps discipline. It provides resources, tools, and training to help organizations implement FinOps. The Foundation also certifies professionals in FinOps, ensuring they have the necessary skills and knowledge to drive success in this domain. For example, the FinOps Certified Practitioner (FOCP) designation is a respected credential that validates an individual’s expertise in FinOps.
Why Is FinOps Adoption Growing? Key Benefits of FinOps
One clear indication of FinOps adoption is membership of the FinOps foundation. Over 5,000 organizations are members, including 48 of the Fortune 50, the world’s largest organizations by revenue. In addition, according to the FinOps Foundation’s latest State of FinOps report, 70% of organizations surveyed have cost optimization policies in place, indicating they are at least partially practicing FinOps. Between 20-55% of organizations report having other elements of FinOps, such as budget alerting policies and resource management policies.
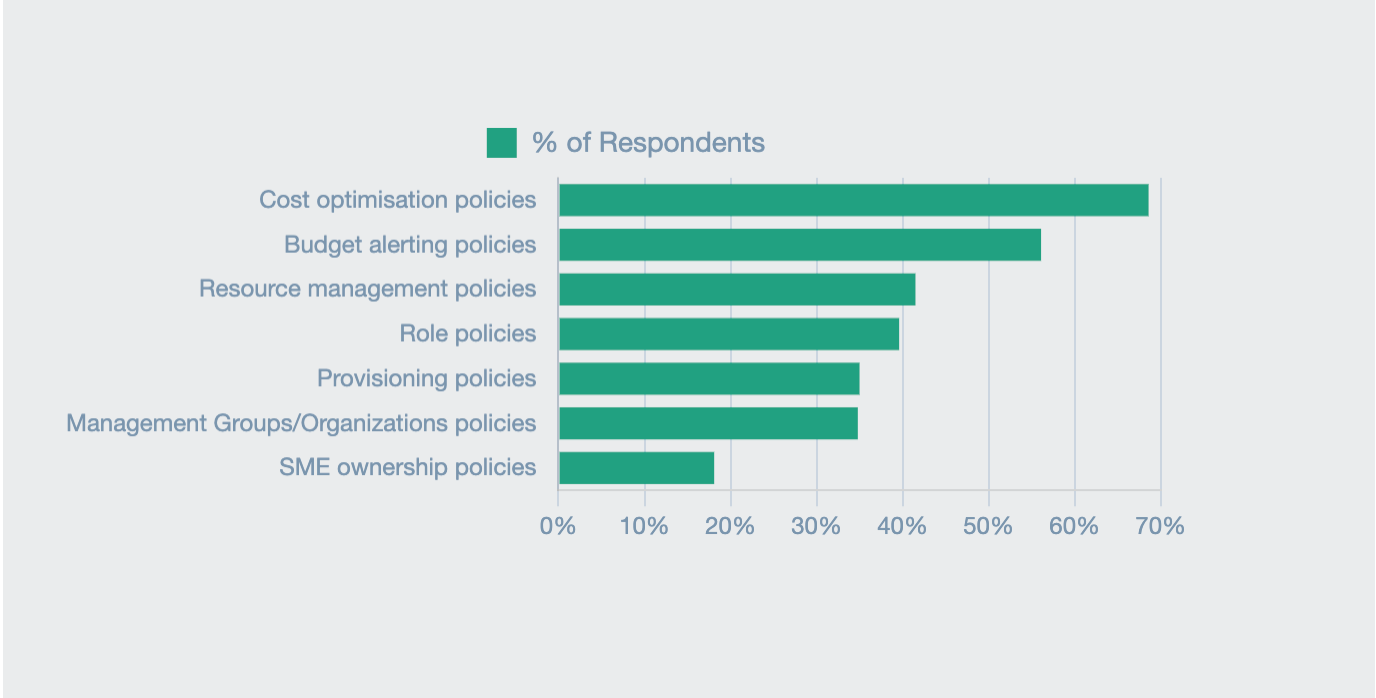
Source: FinOps Foundation
The key benefits driving the rapid adoption of FinOps include:
- Reduced cloud costs: By implementing the principles of FinOps, businesses can gain a better understanding of their cloud usage and costs, identify inefficiencies, and take action to reduce waste. FinOps practices can generate a significant reduction in cloud costs in the long run.
- Improved financial performance: By aligning cloud costs with business value, FinOps helps businesses to make smarter, more strategic decisions about their cloud investments. FinOps can help drive financial performance by optimizing cloud use to maximize return on investment.
- Better decision-making: With its focus on data and reporting, FinOps provides businesses with the insights they need to make informed decisions about cloud usage and expenditure. This leads to better outcomes and higher returns.
- Increased transparency: By promoting collaboration, accountability, and reporting, FinOps creates a culture of transparency around cloud costs. This helps businesses understand and manage their cloud costs more effectively, leading to better financial performance and greater business value.
The Three Pillars of FinOps
There are three essential aspects, or pillars, required to practice FinOps in your organization: Inform, Optimize, and Operate.
Inform
The ‘Inform’ pillar involves creating visibility into cloud costs and usage. It’s about collecting, aggregating, and analyzing data to gain insights into how the cloud is being used and what it’s costing. This visibility allows for better forecasting, budgeting, and planning of cloud spend.
The ‘Inform’ pillar also includes educating all stakeholders about the financial impact of their decisions. When everyone understands the cost implications of their actions, they can make more cost-effective choices.
Optimize
Optimization involves identifying inefficiencies and waste in cloud usage and taking steps to address them. This could mean right-sizing instances, eliminating idle resources, or leveraging discounts from cloud providers.
The ‘Optimize’ pillar is a continuous process, which requires regular monitoring and adjustment to keep cloud costs in check.
Operate
The ‘Operate’ pillar is about putting the insights gained from the ‘Inform’ and ‘Optimize’ pillars into action. This involves implementing changes that will result in cost savings and efficiency improvements. This could mean adjusting resource allocation, changing usage patterns, or renegotiating contracts with cloud providers.

Melissa Abecasis
Director of Customer Success & Sr. Cloud FinOps Engineer, Anodot
Melissa brings a wealth of experience in customer success, cloud financial operations, and program management, with a demonstrated work history in the Information Technology and healthcare industry.
TIPS FROM THE EXPERT
1. Automate cost-saving actions
Use automation tools to shut down idle resources, enforce scaling policies, and implement governance rules that prevent resource sprawl. Automation can handle repetitive tasks, reducing manual interventions and avoiding unnecessary spending.
2. Align cloud costs with business KPIs
Track cloud spend in relation to key business performance indicators. If cloud costs rise while revenue or user growth lags, teams can course-correct to align infrastructure investment with business outcomes better.
3. Optimize reserved instances and savings plans
Maximize savings by combining pay-as-you-go pricing with reserved instances or savings plans. By regularly reviewing usage trends, you can lock in cost-saving contracts and avoid over-committing resources.
4. Foster cross-functional collaboration
Encourage collaboration between finance, engineering, and operations teams by establishing regular FinOps sync meetings. This helps ensure decisions about cloud infrastructure align with both financial goals and technical requirements.
5. Leverage AI-driven FinOps tools
Use AI and machine learning to forecast cloud costs, detect anomalies, and recommend optimizations. AI-driven insights can quickly identify inefficiencies that might otherwise be overlooked, saving significant costs over time.”
The Principles of FinOps
Beyond the three pillars, FinOps has a series of principles that should inform how organizations structure their approach to cloud cost management.
Team Collaboration
In a traditional organization, finance and operational teams often operate in silos, with little interaction between them. However, FinOps necessitates a breakdown of these silos, fostering a culture of collaboration and communication.
By adopting a FinOps approach, organizations are encouraged to view finance and operations as a shared responsibility. It encourages teams to work together towards common goals, ensuring a more efficient process. This collaborative approach also leads to improved decision-making, as teams can leverage their collective knowledge and expertise.
Ownership
In traditional business structures, the onus of financial management typically falls on the finance department. However, FinOps promotes a sense of shared ownership.
In the FinOps framework, all team members, regardless of their department or role, are encouraged to take responsibility for financial outcomes. This sense of ownership not only fosters accountability but also drives better decision-making across the board. When everyone feels a sense of ownership, they are more likely to make decisions that will positively impact the organization’s financial performance.
Business-Driven Decisions
FinOps is not just about managing finances; it’s about aligning financial operations with business objectives. In a FinOps-driven organization, all decisions, whether they relate to budget allocation, resource management, or operational strategies, are driven by the overarching business goals.
By making business-driven decisions, organizations can ensure that their financial strategies are in sync with their goals, ultimately driving better business performance.
Timely Reporting
In traditional financial management, reporting is often a monthly or quarterly exercise. With FinOps, there’s a shift towards real-time, or at least timely, reporting. This allows for quicker decision-making and more proactive management of resources.
Timely reporting also ensures transparency, a key element in the FinOps framework. By having access to up-to-date financial data, teams can make informed decisions that align with the organization’s financial goals and objectives.
Centralized Leadership
While FinOps encourages a sense of shared ownership, it also recognizes the need for centralized leadership. A strong leadership team is crucial for driving the FinOps agenda, setting the vision, and ensuring that all teams understand and adhere to the principles of FinOps.
Centralized leadership is also key in establishing and enforcing processes and policies. This ensures consistency across the organization, which is crucial for the successful implementation of FinOps.
Variable Cost Models
One of the major shifts in the digital age is the move towards cloud computing. The FinOps framework embraces this shift, encouraging organizations to take advantage of the variable cost model of the cloud.
By leveraging the cloud, organizations can scale their resources up or down based on need, leading to significant cost savings. This flexibility allows organizations to better manage their resources and align their financial operations with their business needs.
What Are FinOps Tools?
FinOps tools are specialized software solutions designed to help organizations implement FinOps practices efficiently. These tools provide functionalities for tracking, analyzing, and optimizing cloud spend, enabling better financial management of cloud resources.
FinOps tools are integral to achieving transparency, accountability, and cost-efficiency in cloud investments. They automate the collection and reporting of cloud usage data, facilitate cost allocation and chargeback, and offer insights for cost optimization. By providing real-time data on cloud spending and usage, FinOps tools enable these teams to make informed decisions quickly, in line with the FinOps principles.
Learn more in our detailed guide to Finops solutions (coming soon)
Key Features of FinOps Tools
Here are the main features you should look for in a FinOps platform:
Cost Management Dashboard
A cost management dashboard is a critical feature in FinOps tools, providing a comprehensive view of cloud spending across different dimensions such as time, service, and organizational structure. It aggregates data from various sources to present a real-time overview of expenditures, allowing for immediate insight into cost trends, anomalies, and opportunities for optimization.
This dashboard is essential for stakeholders at all levels to monitor cloud costs effectively, identify potential overspending areas, and make informed decisions to control expenses. The ability to customize views and set up alerts for budget thresholds ensures that spending remains within planned limits, promoting fiscal discipline while maximizing cloud investment value.
Cost Allocation and Chargeback
Cost allocation and chargeback mechanisms are key features of FinOps tools, enabling organizations to accurately track and distribute cloud costs to the responsible departments or projects. This process involves tagging resources with metadata that identifies their ownership and purpose, allowing for precise cost tracking and accountability.
By implementing a detailed chargeback model, organizations can foster a culture of cost awareness and responsibility, encouraging teams to optimize resource usage and reduce unnecessary expenditures. This feature not only ensures fair billing practices but also aligns cloud spending with business objectives, making it easier to evaluate the financial impact of different initiatives.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting functionalities within FinOps tools are crucial for effective financial planning and control. These features allow organizations to set budgetary limits based on historical data, projected growth, and strategic objectives. Forecasting capabilities enable predictive analysis of future spending patterns, helping to anticipate and mitigate risks associated with cloud cost escalation.
By integrating these financial planning tools with real-time cost data, businesses can dynamically adjust their strategies to remain on target, ensuring financial sustainability and operational efficiency in their cloud investments.
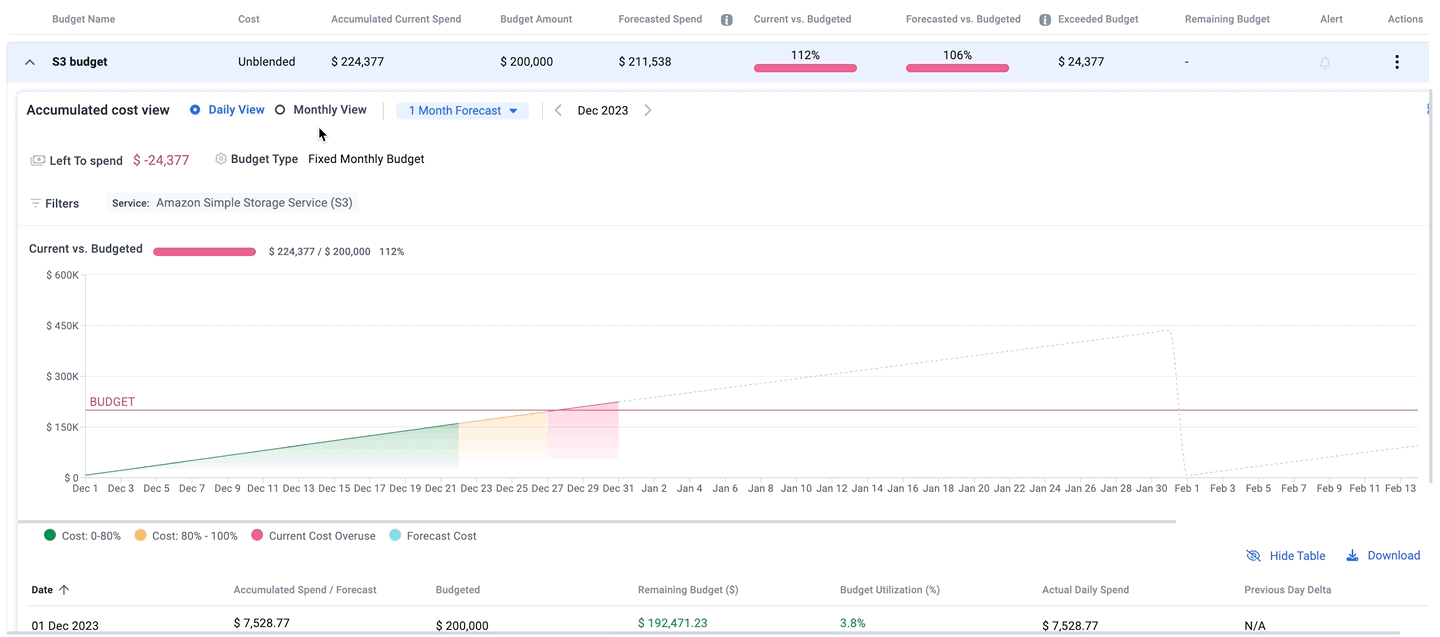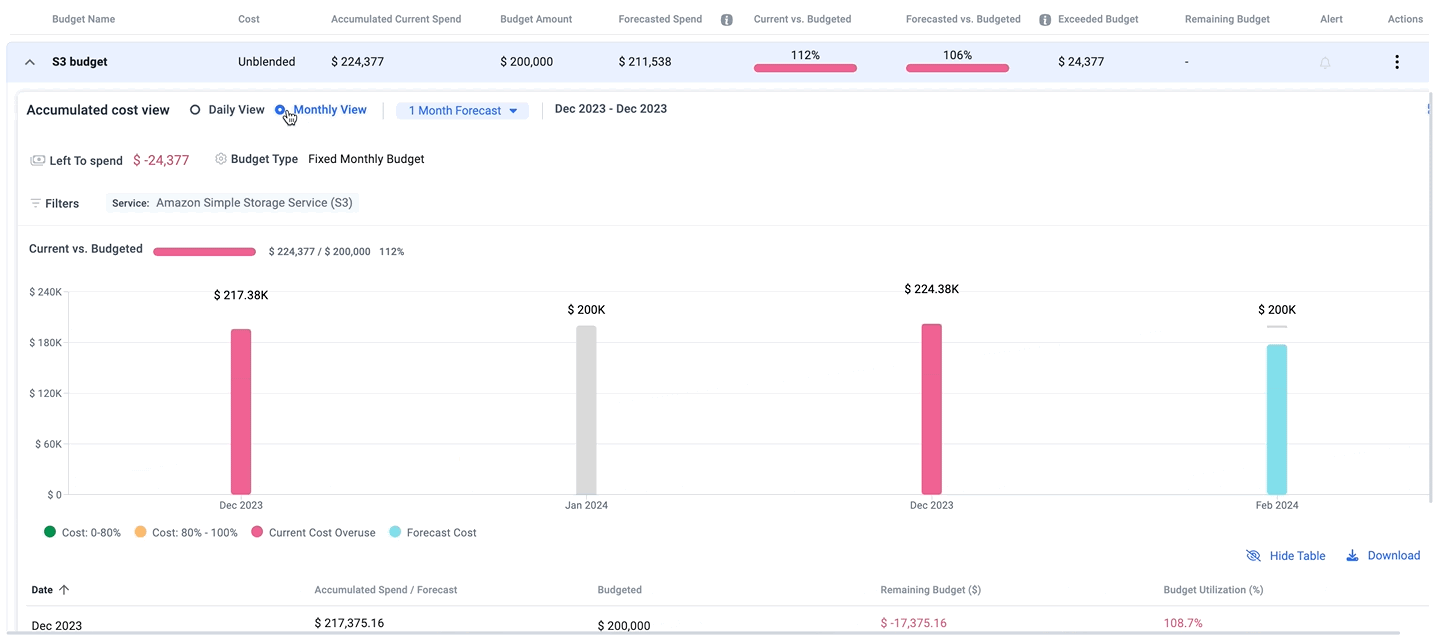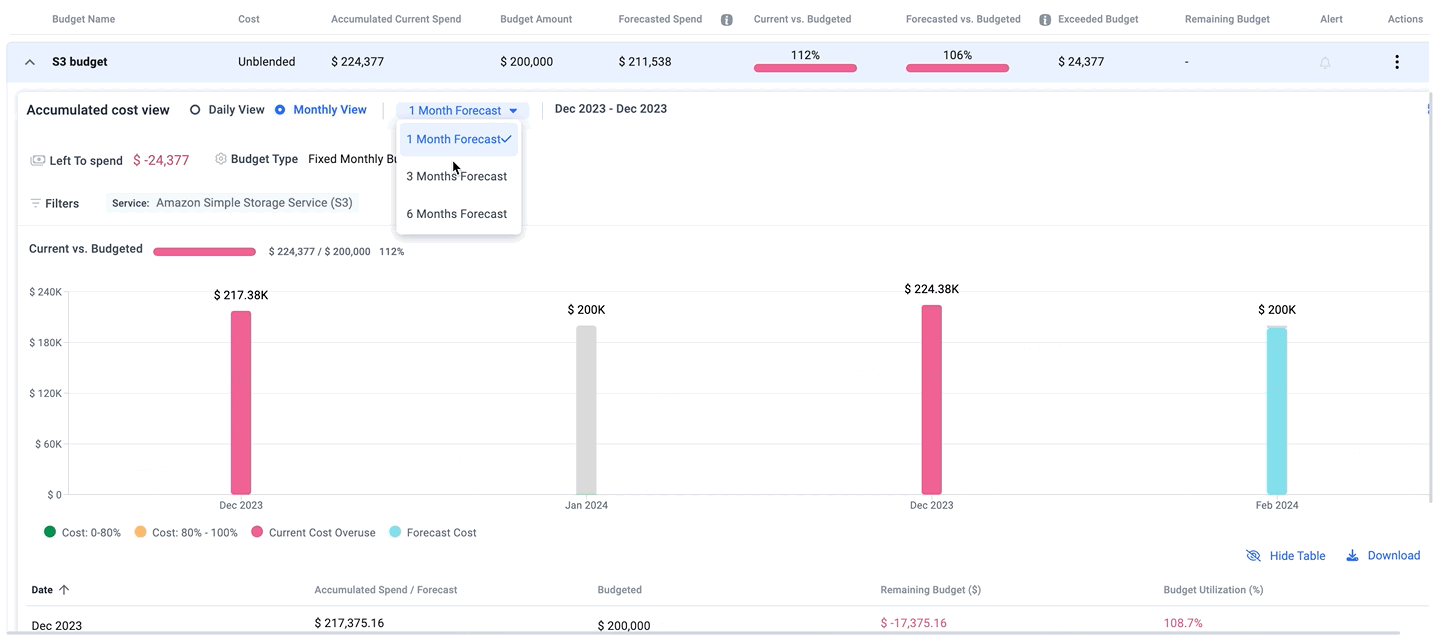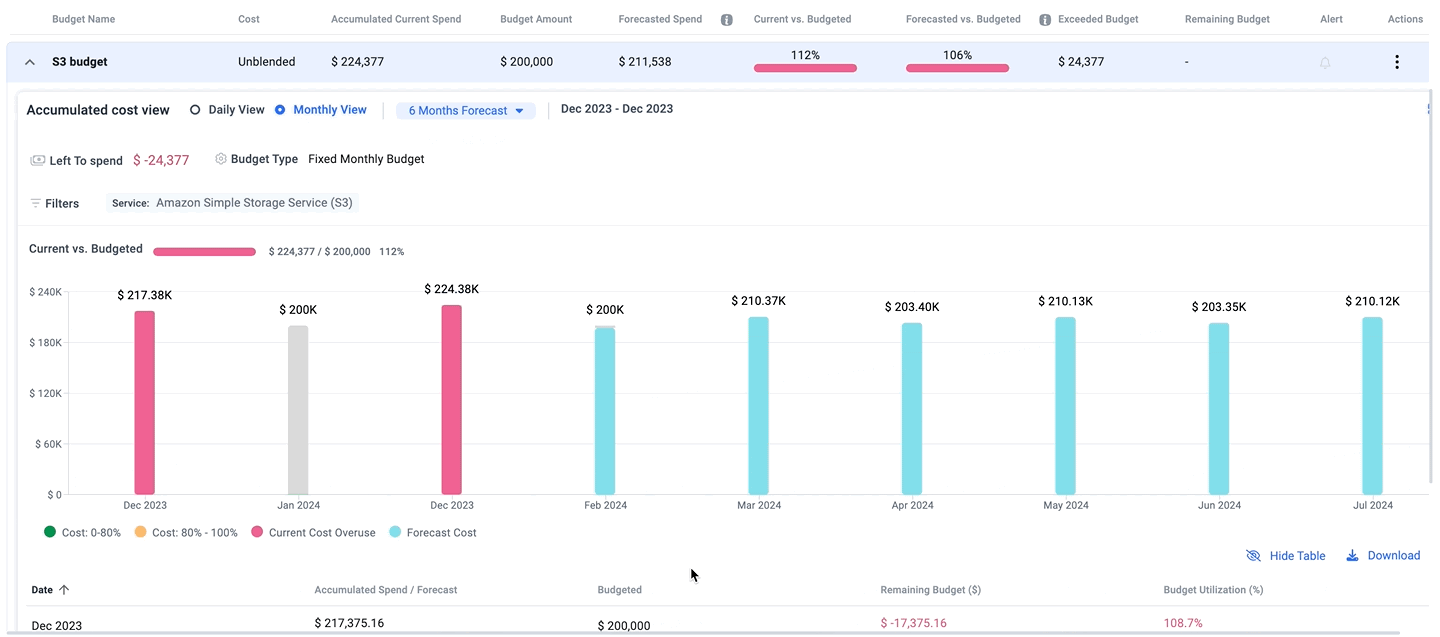
Integration with Cloud Providers
Integration with cloud providers is a fundamental feature of FinOps tools, enabling data collection and analysis across multiple cloud platforms. This capability allows organizations to consolidate billing and usage information from different providers into a unified dashboard, facilitating a comprehensive view of cloud expenses.
Direct integration with cloud service APIs ensures accurate and up-to-date data retrieval, essential for effective cost management and optimization efforts. By leveraging these integrations, businesses can streamline operations, reduce administrative overhead, and enhance decision-making processes related to cloud resource allocation and financial planning.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) Analysis
Traditional cost monitoring technologies are largely reactive in nature. They typically rely on static alert thresholds, dashboards, and reports. Similarly, the tools offered by cloud or advertising providers often have at least a 24 hour delay in the availability of data.
Advanced FinOps tools use AI/ML to tackle the inherent complexity of business metrics. Machine learning models make it possible to monitor 100% of the data in real time, track each individual metric’s normal behavior autonomously, and correlate each metric with the others using deep root cause analysis. This results in faster time-to-detection and time-to-resolution.
Related content: Read our guide to cloud cost monitoring
KPIs for Measuring FinOps Success
When implementing FinOps in your organization, it’s important to track your progress. Here are a few metrics that can help you evaluate how FinOps is contributing to your business performance.
Percentage of Allocatable Cloud Spend
This metric looks at how much of your cloud spend can be directly attributed to specific resources or projects. It’s an important KPI because it provides insight into how efficiently your organization is utilizing its cloud resources.
A high percentage of allocatable cloud spend indicates that you’re able to effectively account for most of your cloud costs. It means you’re effectively managing your cloud resources, which is a key aspect of FinOps. Conversely, a low percentage could suggest inefficiency, requiring you to delve deeper into your cloud usage and make necessary adjustments.
Average Hourly Cost
This KPI refers to the average amount spent per hour on cloud resources. It’s a straightforward way to track cloud spending and can help identify trends or anomalies.
A consistent average hourly cost suggests efficient cloud resource management. If the average hourly cost is fluctuating significantly or increasing over time, it could be a sign of inefficiency. This might mean that you’re not optimally using your cloud resources or that there are unexpected costs creeping in.
Cloud Unit Costs
Another vital KPI in FinOps is cloud unit costs. This refers to the cost of a specific unit of cloud resource, such as a gigabyte of storage or an hour of compute time. Monitoring cloud unit costs allows you to track the cost-effectiveness of your cloud usage.
If your cloud unit costs are increasing, it might suggest that you’re not getting the best value for your cloud spend. On the other hand, decreasing cloud unit costs could indicate that you’re becoming more efficient in your cloud usage.
Percentage of Waste
This KPI measures the proportion of cloud resources that are being paid for but not utilized. This could include idle compute resources, under-utilized storage, or unnecessary network capacity. It’s a direct measure of inefficiency and an area where significant cost savings can often be found.
A high percentage of waste suggests that you’re not getting the most out of your cloud spend. Reducing waste should be a priority in any FinOps strategy, as it’s a straightforward way to reduce costs without impacting the services you provide.
Forecasting Accuracy
Forecasting accuracy is a measure of how closely your predicted cloud spend matches your actual spend. This KPI directly impacts budgeting and financial planning.
High forecasting accuracy indicates effective financial management and suggests that you’re able to predict and control your cloud costs effectively. Poor forecasting accuracy, however, can lead to budget overruns and financial uncertainty. Improving forecasting accuracy should be a key part of your FinOps strategy.
Best Practices to Implement a FinOps Program
Let’s look at some best practices to help you implement a successful FinOps strategy.
Build a Cross-Functional Team
The FinOps team should be composed of individuals from various departments within the organization. This includes finance, IT, operations, and any other relevant department. The cross-functional team can bring together diverse perspectives and skillsets, which can help in identifying and addressing potential challenges in the FinOps implementation process.
Establishing this team demands a strong leadership commitment because it often requires breaking down siloed structures within the organization and fostering a culture of collaboration. Leaders must ensure that all team members understand the overarching goals of the FinOps program and the role they play in achieving these objectives.
Create a Resource Tagging Strategy
Resource tagging involves applying tags to categorize resources based on various parameters such as cost center, project, or environment. It can significantly simplify resource management and cost allocation.
Establish a consistent tagging taxonomy by defining a set of standard tags and ensuring their consistent application across all resources. This will facilitate more effective tracking and reporting processes.
Establish Budgets and Forecasts
Budgeting involves the allocation of resources based on anticipated revenues and expenses. Forecasting is the process of estimating future financial outcomes based on historical data and market trends.
The success of financial planning largely depends on the accuracy of the data used. Ensure that the data used is up-to-date and accurately reflects the organization’s financial status. Advanced FinOps tools that leverage AI/ML analysis can help improve forecast accuracy and perform deeper analysis of business metrics.
Optimize Existing Resources
Resource optimization involves the efficient use of available resources to maximize their potential and ensure cost-effectiveness. It’s a process that requires a deep understanding of the organization’s resources and how they are currently utilized.
Use analytics to gain insights into resource usage patterns and identify potential areas for improvement. For instance, you might discover that some resources are underutilized and others are overutilized, providing opportunities for reallocation and cost savings.
Leverage Automation
Incorporating automation into FinOps practices helps enhance efficiency and reduce manual effort in cloud cost management. Automation tools can be used to streamline processes such as cost reporting, budget tracking, and resource provisioning.
Automation can also play a significant role in enforcing policies and compliance. For example, automated scripts can be set up to shut down or scale down underutilized resources, ensuring that cloud spending is kept in check. Automation can aid in the implementation of governance rules, ensuring that all cloud deployments adhere to organizational standards and budget constraints.
Learn more in our detailed guide to FinOps best practices (coming soon)
Anodot’s FinOps Solution
Anodot’s cloud cost management solution helps businesses understand cloud unit economics by aligning cloud costs to key business dimensions. This allows users to track and report on unit costs and get a clear picture of how infrastructures and economies are changing.
Anodot’s cost allocation feature helps organizations accurately map multicloud and Kubernetes spending data, assign shared costs equitably, and drive FinOps collaboration throughout your organization.
With Anodot, FinOps teams can easily classify and divide all of their cloud costs by business structures like apps, teams, and lines of business. Inform and empower business decisions at all levels from Anodot’s cloud cost management solution.
See Additional Guides on Key DevOps Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of DevOps.
Cloud Cost Optimization
Authored by Anodot
- Top 13 Cloud Cost Optimization Best: Practices for 2024
- What Is Cloud Computing TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)?
- The 4 Factors Influencing Cloud Spend & 6 Ways to Optimize It
Continuous Delivery
Authored by Codefresh
- What Is Continuous Delivery and How Does It Work?
- Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment
- Continuous Delivery Pipeline: The 5 Stages Explained
Documentation Tools
Authored by Swimm




