What Is AWS Cost Management?
AWS cost management is the systematic practice of monitoring, controlling, and optimizing expenditure on Amazon Web Services (AWS). It involves tracking and analyzing cloud usage, identifying areas where spending can be reduced, and implementing strategies to manage and optimize costs. This practice is essential for organizations to ensure that their cloud spending aligns with their budgetary constraints and business objectives.
Effective AWS cost management requires a combination of tools and practices. Organizations need to continuously monitor their usage patterns, understand the pricing models of different AWS services, and leverage tools that provide insights into cost and usage data. This helps make informed decisions, such as rightsizing instances, optimizing storage, and taking advantage of reserved instances and savings plans to lower costs.
After covering the basics, we’ll help you master AWS cost management by presenting tools that can help automate AWS cost management and strategic best practices you can use to bring AWS costs under control.
In this article:
- The Benefits of AWS Cost Management
- Challenges of Managing AWS Costs
- Free AWS-Native Cost Management Tools
- Third-Party AWS Cost Management Tools
- Strategies and Best Practices for Reducing AWS Cost
The Benefits of AWS Cost Management
By practicing AWS cost management, your organization gains the following benefits:
- Cost visibility: Ability to track expenses across different services, identify trends in usage, and pinpoint areas where costs can be optimized. This ensures a clear understanding of the organization’s cloud expenditure, informing data-driven decisions on how to allocate resources.
- Cost efficiency: By analyzing spending patterns and comparing them against operational requirements, companies can uncover opportunities for cost savings—such as terminating unused instances or scaling down over-provisioned services. This reduces waste and enhances the efficiency of cloud operations.
- Monitoring and alerts: Continuous monitoring of cloud expenditures allows organizations to track their spending in real time. This allows them to quickly identify and respond to cost-related issues as they arise. Alerting can notify users when spending exceeds predefined thresholds or when spending anomalies occur.
- Resource optimization: By understanding usage patterns and resource configurations, organizations can identify instances where resources are underutilized or oversized. Adjusting these resources to better match actual needs can lead to significant cost savings without impacting performance or availability.
Challenges of Managing AWS Costs
There are also several challenges involved in managing costs in AWS:
- Cost accountability: In environments where multiple teams or departments utilize AWS resources, pinpointing cost accountability becomes challenging. It is difficult to control cloud spending without clear visibility into which team or project is consuming resources.
- Understanding the AWS bill: Each line item reflects the consumption of a specific service, such as Amazon EC2 instances or S3 storage, including the quantity used, the rate charged, and the total cost. In large-scale AWS deployments, the combined set of AWS bills can be difficult to navigate, with a complex structure of AWS pricing models and service billing items.
- Accurately forecasting AWS costs: This involves understanding the organization’s usage patterns and how they translate into expenses. The variable nature of AWS services and pricing options makes accurate forecasting complex.
- Identifying saving opportunities: It can be difficult to identify waste or pinpoint savings opportunities in a large-scale AWS environment. Automated tools are needed to scan the entire environment, compare available pricing options, and suggest optimizations.
Related content: Read our guide to AWS cost optimization

Melissa Abecasis
Director of Customer Success & Sr. Cloud FinOps Engineer, Anodot
Melissa brings a wealth of experience in customer success, cloud financial operations, and program management, with a demonstrated work history in the Information Technology and healthcare industry.
TIPS FROM THE EXPERT
1. Create cost-aware development practices
Integrate cost management into your DevOps workflows by making engineers aware of the financial impact of their infrastructure choices. Encourage the use of cost-efficient services and resources during the development process.
2. Incorporate cost metrics into business KPIs
Align your AWS cost management efforts with broader business objectives by incorporating cost metrics into your key performance indicators (KPIs). This ensures that cost management is viewed as a strategic priority rather than just an operational concern.
3. Maximize savings with mixed instance types
Use a combination of on-demand, reserved, and spot instances in your auto-scaling groups. This mixed approach balances cost savings with the need for flexibility and availability, especially in variable workloads.
4. Monitor and optimize data transfer costs
Keep a close eye on data transfer charges, especially across regions or out of AWS.
5. Use third-party tools for advanced cost insights
Complement AWS native tools with third-party cost management solutions like Anodot or CloudCheckr. These tools offer advanced analytics, multi-cloud support, and more granular reporting, helping you uncover deeper cost-saving opportunities.
Free AWS-Native Cost Management Tools
Most organizations start their cost management journey with tools built into the AWS environment, which provide a basic level of cost management at no cost.
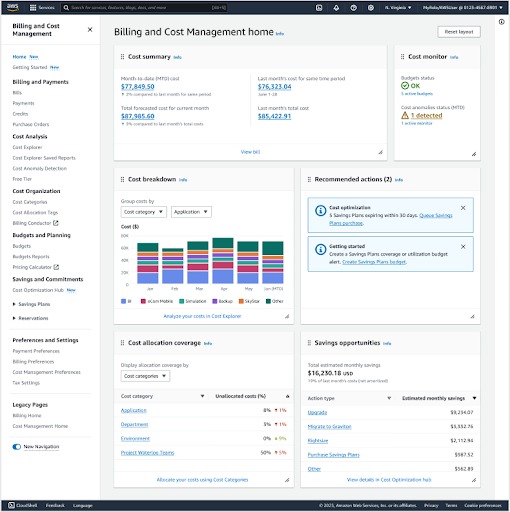
1. AWS Billing and Cost Management
AWS Billing and Cost Management is a comprehensive suite that allows users to access and manage their AWS spending and usage. Through this service, customers can view detailed billing reports, set up budget alerts, and analyze costs to identify saving opportunities. It provides a centralized dashboard for monitoring all AWS charges in one place.
This tool also supports cost allocation through tagging, enabling organizations to attribute expenses to specific projects or departments. By leveraging the detailed reporting and cost analytics features, organizations can gain deeper insights into their cloud expenditure patterns.
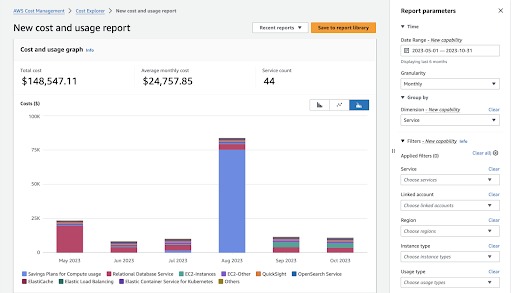
2. AWS Cost Explorer
AWS Cost Explorer is a tool within the AWS Management Console that enables users to visualize and manage their AWS spending. It provides detailed insights into past usage patterns, facilitating accurate forecasting of future expenditures. Users can drill down into their costs based on various dimensions such as service, geography, and time period.
Cost Explorer allows users to set custom reports that track specific metrics or financial goals. Organizations can tailor their cost management strategies to meet unique business requirements. Features like Anomaly Detection automate identifying unusual spending activities, alerting users to potential inefficiencies or unexpected charges.
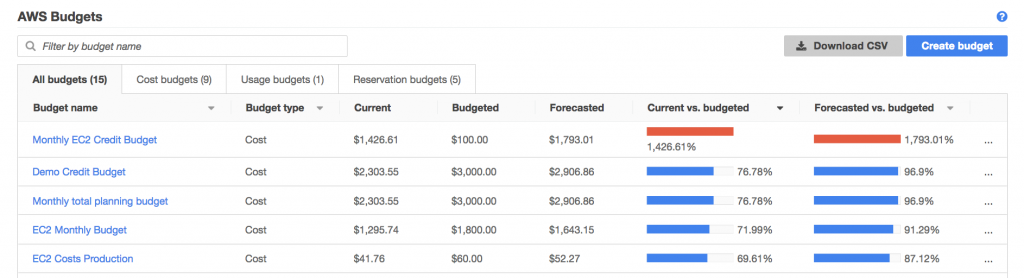
3. AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets allows users to proactively manage cloud costs by setting custom budget thresholds and receiving alerts when spending exceeds these limits. This tool helps in maintaining financial discipline, allowing organizations to allocate their AWS expenses without the risk of overspending, and defining budgets for specific services, projects, or departments.
The service enables real-time monitoring of expenses against established budgets, providing notifications that enable swift corrective actions. AWS Budgets supports various budgets—cost-based, usage-based, RI (Reserved Instance) utilization, and Savings Plans utilization—offering flexibility in how organizations track and manage their AWS spending.
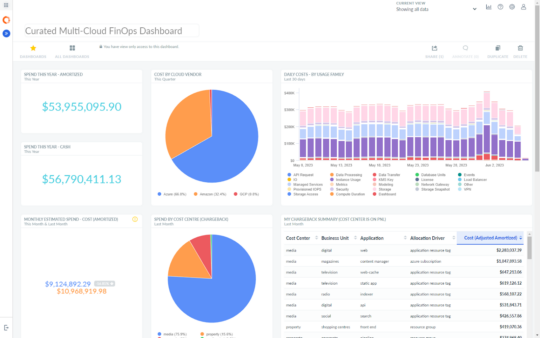
Third-Party AWS Cost Management Tools
The following tools take cost management one step further, offering more advanced capabilities and enabling cost management across multiple clouds.
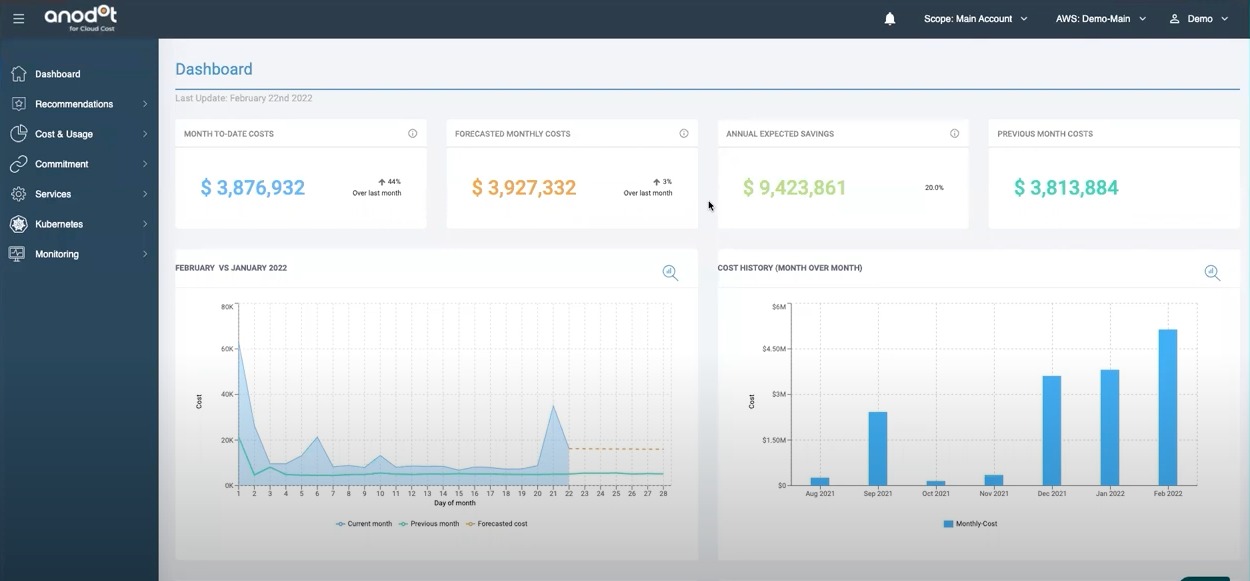
4. Anodot
Anodot for AWS Cost Management provides real-time visibility, continuous monitoring, and precise cost forecasting for AWS expenditures. Leverage Anodot’s user-friendly suggestions across any cloud platform to gain up to 40% savings on annual AWS expenses.
Leading companies such as Amdocs, NICE, and Fiverr trust Anodot for AWS Cost Management to oversee, optimize, and reduce AWS costs through various savings recommendations.
Features:
- Seamless integration: Easily connect your AWS account to Anodot in minutes and 5-click integration requiring minimal permissions.
- Detailed cost insights: Receive accurate cost breakdowns within 24 hours of setup.
- Holistic overview: Consolidate costs from multiple AWS service providers on a single platform.
- Tailored analytics: Create customized reports and interactive dashboards.
- Sharing capabilities: Effortlessly export reports and collaborate with diverse teams.
- In-depth analysis: Quickly identify potential opportunities for cost savings.
- Anomaly detection for comprehensive cost reports: Obtain autonomous analytics for real-time business monitoring, enabling early detection of unidentified issues for seamless operations.
Try Anodot for Cost FREE for 30 days
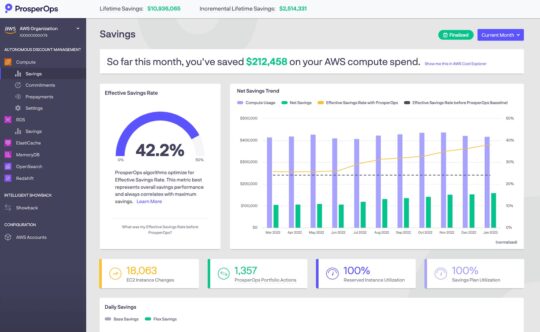
5. ProsperOps
ProsperOps offers an automatic cloud cost optimization solution specifically designed for AWS. This solution autonomously manages pricing optimization for several AWS services, including compute, RDS, Redshift, ElastiCache, OpenSearch, and MemoryDB. It also provides automated financial reports in standard accounting formats.
Features:
- Leveraging discounts: Automatically optimizes AWS and Google Clouds discounts in real time. Provides algorithms designed to maximize discounts while minimizing long-term commitment risks associated with inelastic services.
- Dynamic adjustments: The platform offers savings of 50% or more off on-demand rates through short and flexible commitments.
- Minimizing commitment risk: Adapts to changes in usage patterns. This is especially useful for organizations experiencing fluctuating demand or undergoing rapid growth, as it ensures that commitments do not become a financial burden.
- Performance-based pricing: ProsperOps fees are based on savings realized by use of its optimization service.
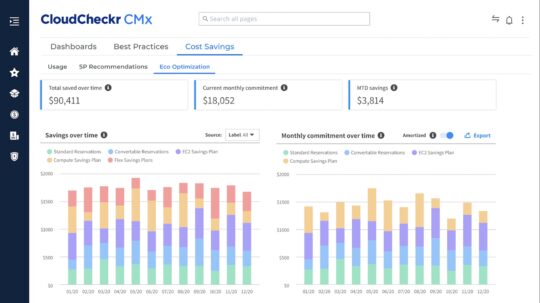
6. CloudCheckr
CloudCheckr, now owned by Spot by NetApp, is a cloud management solution for FinOps and governance. It supports large enterprises and managed service providers (MSPs) in managing and reducing cloud costs, optimizing resources for efficiency, enhancing governance practices, and strengthening security and compliance measures.
Features:
- Visibility into the cloud spend: Offers insights into current and historical cloud spending, enabling users to understand which services are driving costs and how resources are utilized across the organization.
- Cost optimization capabilities: Provides tools for reducing cloud spend through right-sizing recommendations and purchase options for commitment discounts.
- Resource efficiency assessment: Tracks long-term consumption trends to pinpoint wasteful expenditures. It assists in identifying underused resources.
- Accurate cost allocation: Enables precise chargeback/showback mechanisms to manage costs and ensure accountability within an organization.
- Security & compliance improvement: Reduces risk by automatically detecting infrastructure misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. Some issues can be resolved through self-healing automation provided by CloudCheckr.
7. Apptio Cloudability
Apptio Cloudability is a cloud cost management and optimization platform that helps IT, finance, and DevOps teams collaborate more effectively. By providing detailed insights into cloud spending and utilization, Cloudability helps organizations allocate resources more efficiently, optimize costs, and improve financial accountability.
Features:
- Cost allocation: Allows users to fully allocate all their cloud spend, including intricate costs like containers and support charges.
- Optimization recommendations: Identifies rightsizing opportunities across major cloud services. This enables organizations to reduce operating expenses by ensuring resources are scaled to actual needs.
- Financial planning tools: Helps organizations forecast future costs with greater accuracy. This aids in strategic decision-making by providing a clear picture of how upcoming projects or scaling efforts will impact overall cloud expenditures.
- Team ownership: Offers views tailored for different stakeholders – from IT finance managers establishing budgets to DevOps teams monitoring resource usage. These role-specific insights encourage proactive management of costs and resource optimization within each team’s domain.
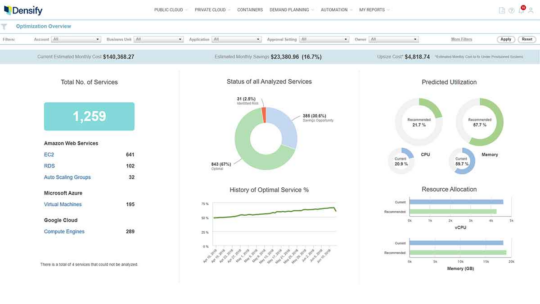
8. Densify
Densify offers a cloud resource optimization solution that uses machine learning and analytics to utilize the most efficient instance types and resources for each workload. This approach automates the process of identifying appropriate configurations for cloud resources, enabling better alignment with application needs.
Features:
- Automated instance selection: Uses machine learning algorithms to analyze workload patterns and automatically determine the most suitable size and family for compute and database instances.
- Optimization of auto scaling groups: Analyzes utilization and scaling behaviors to ensure auto scaling groups are correctly configured for elasticity.
- Capacity visibility across clouds: Provides a unified view of cloud health. Users can compare efficiency ratings, identify savings opportunities, assess risks, and estimate financial impacts across different cloud environments.
- Collaborative optimization reporting: Generates reports on optimization recommendations for sharing with stakeholders. These reports include predicted utilization, effort level required for changes, and potential cost impacts.
Strategies and Best Practices for Reducing AWS Cost
Here are some of the ways that organizations can reduce their costs in AWS, and how to get started with these practices using AWS native tools.
1. Identify Unnecessary Instances
Identify and address underutilized EC2, RDS, and Redshift instances. Begin by monitoring their usage metrics to pinpoint those that are consistently underutilized. AWS provides tools like CloudWatch and Trusted Advisor to help track CPU utilization, memory usage, and network activity.
If an instance shows low utilization over time, consider stopping it or switching to a smaller instance type. This right-sizing approach ensures you pay only for the needed resources, aligning costs with actual usage.
2. Delete Unnecessary Volumes and Snapshots
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes can quickly become a source of unnecessary costs if not properly managed. Regularly review your EBS volumes to identify those with low or no I/O activity over a period. Unused or underutilized volumes should be detached and deleted to avoid incurring storage charges. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer can help visualize EBS usage patterns, making it easier to spot inefficiencies.
Additionally, orphaned snapshots—snapshots without any associated EBS volumes—often accumulate over time and contribute to increased storage costs. Conduct periodic audits using AWS Console or automated scripts to detect and remove these orphaned snapshots.
3. Take Advantage of Amazon S3 Storage Tiers
Start by categorizing your data based on access frequency and retention requirements. Frequently accessed data should remain in the standard S3 storage class. However, infrequently accessed data can be moved to cheaper storage tiers like S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent Access) or S3 Glacier for archival purposes.
AWS provides Storage Class Analysis tools to help identify data that is a candidate for transition to lower-cost storage classes. Consider enabling S3 Lifecycle Policies to automate data movement. These policies can automatically transition objects to more cost-effective storage classes or delete them after a specified period.
4. Optimize Networking and Load Balancing
AWS load balancers, including Elastic Load Balancers (ELBs) and Application Load Balancers (ALBs), can incur significant costs if not properly managed. Regularly review your load balancer usage to identify those with minimal or no traffic.
AWS CloudWatch metrics can help monitor request counts and latency. If a load balancer is idle or unnecessary, consider deleting it to eliminate its associated costs. Optimizing the configuration of active load balancers can also contribute to cost savings. Ensure that load balancers are correctly sized and configured to match the traffic they handle.
5. Use Spot Instances to Reduce Costs
Spot instances offer significant cost savings by allowing you to use spare AWS compute capacity at reduced rates. These instances can be up to 90% cheaper than on-demand instances, making them suitable for flexible and fault-tolerant workloads. Use spot instances for batch processing, data analysis, or any application that can handle interruptions.
Tools like EC2 Auto Scaling groups with mixed instances and Spot Fleet can help manage spot instances. For Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), configure your Kubernetes clusters to use spot instances for worker nodes. For EMR, take advantage of the flexibility spot instances offer for running big data applications.
6. Use and Manage Reserved Instances
Reserved instances (RIs) provide cost savings compared to on-demand Instances by allowing you to commit to using specific instance types in particular regions for a one- or three-year term. Analyze your long-term usage patterns to determine which instances are suitable for RIs. AWS Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor can recommend RI purchases based on historical usage data.
Make sure these instances are fully utilized. If you have purchased RIs that are no longer needed, AWS provides a marketplace where you can sell unused RIs. This can help recover some of the costs associated with RIs that are no longer used.
7. Use Compute Savings Plans
AWS Compute Savings Plans offer a flexible pricing model that significantly saves EC2, Fargate, and Lambda usage. Unlike RIs, Savings Plans apply automatically to any compute usage, regardless of instance family, size, or region. This flexibility makes it easier to achieve cost savings even as compute needs change over time.
First, analyze your historical compute usage to estimate potential savings and determine an appropriate commitment level. AWS provides tools like Cost Explorer to visualize past usage and simulate savings under different Savings Plan scenarios. By committing to consistent usage over one- or three-year terms, organizations can save up to 72%.
8. Choose the Right AWS Region
Different regions have varying pricing structures for the same services. When deploying resources, compare the costs across regions to identify the most cost-effective location that meets your performance and compliance requirements. Tools like AWS Pricing Calculator can help estimate costs in different regions, making it easier to make informed decisions.
In addition to cost considerations, latency and data transfer charges associated with different regions should be assessed. Placing resources closer to the user base can reduce latency and improve performance while also minimizing data transfer costs.
Limitations of AWS Native Cost Management Tools
AWS-native tools offer a first line of defense for managing your cloud costs, but don’t cover all the functionality you need to succeed at FinOps. They have the following key limitations:
- No multi-cloud support: AWS offers little insight for businesses with modern multi-cloud strategies, ignoring the existence of other public clouds.
- Functionality gaps: AWS native tools have many functionality gaps, including limited reporting, cost optimization, and cost allocation—and no support for Kubernetes or conversational FinOps.
- Licensing: AWS native tools have certain limitations depending on the type of license and support plan used by the organization—not all features are available for every plan. For example, if you are on the AWS Basic or Developer Support plans, you can only use the Trusted Advisor console to access all checks in the Service Limits category and six checks in the Security category. You cannot access the cost optimization, performance, or fault tolerance check categories.
A purpose-built FinOps solution like Anodot can fill these gaps and add value across the enterprise. Anodot is a next-generation certified FinOps platform that enables successful FinOps with a holistic and augmented approach. Anodot provides comprehensive coverage for all FinOps domains, enabling organizations to rapidly mature their FinOps practices so they can deliver the highest business value.