What Is Cloud Optimization?
Cloud optimization refers to adjusting your cloud environment and resources to improve efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. It involves analyzing current usage, identifying inefficiencies, and changing resource allocation, configurations, and services to match your needs better. This process helps organizations maximize their cloud investment by ensuring resources are used most effectively.
Cloud optimization aims to reduce costs and enhance the performance and scalability of applications running in the cloud. By continuously monitoring and optimizing the cloud environment, businesses can respond more quickly to changing demands, avoid over-provisioning, and ensure that their applications run smoothly and efficiently.
Below is an example of cloud optimization. This dashboard provides recommendations for upgrading, stopping, or right-sizing cloud resources to optimize cost.
Learn more about the cloud cost management platform from Anodot, which provides cost optimization recommendations.
This is part of a series of articles about cloud management.
In this article:
- Why Is Cloud Optimization Important?
- What Should You Optimize in Your Cloud Environment?
- Types of Cloud Optimization Services and Tools
- Challenges in Cloud Optimization
- Best Practices to Optimize Your Cloud Environment
Why Is Cloud Optimization Important?
Cloud optimization is crucial because it directly impacts an organization’s bottom line and operational efficiency. Without proper optimization, companies can end up paying for unused or underutilized resources, leading to unnecessary expenses. According to the HashiCorp State of Cloud Strategy Survey, over 90% of companies believe they are spending too much on the cloud.
According to Gartner, public cloud spending was almost $600 billion in 2023, showing how large the problem is. Optimizing the cloud environment ensures that resources are allocated according to actual needs, reducing waste and lowering costs.
What Should You Optimize in Your Cloud Environment?
Cost-Effectiveness
Optimizing for cost-effectiveness involves identifying and eliminating waste in your cloud spending. This means turning off idle resources, choosing the right size and type of resources for your workload, and taking advantage of discounts offered by cloud providers for commitments or reserved instances. Effective cost management ensures you only pay for what you need and use.
Furthermore, organizations can significantly reduce costs by analyzing usage patterns and adopting a pay-as-you-go model. Implementing policies for budget management and cost allocation helps manage spending and make informed decisions about resource utilization.
Performance
Performance optimization ensures your applications run efficiently and respond quickly to user demands. This involves selecting the right types of resources for your workloads, configuring your environment to maximize resource utilization, and scaling resources dynamically based on demand. By optimizing for performance, you can improve user satisfaction and engagement with your applications.
Implementing caching, using content delivery networks (CDNs), and optimizing databases are crucial strategies. These adjustments help reduce latency, improve load times, and ensure that your applications can handle high traffic volumes without degradation in performance.
Reliability
Security optimization in the cloud involves strengthening your environment against vulnerabilities and threats. This means implementing robust access controls, encrypting data at rest and in transit, and regularly monitoring and auditing the environment for suspicious activities. Optimizing security helps protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Adopting a security-first mindset and leveraging automated security tools can significantly reduce the risk of breaches. Continuous vulnerability assessments and integrating security into the development lifecycle are also crucial components of a strong cloud security posture.
Security
Security optimization in the cloud involves strengthening your environment against vulnerabilities and threats. This means implementing robust access controls, encrypting data at rest and in transit, and regularly monitoring and auditing the environment for suspicious activities. Optimizing security helps in protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Adopting a security-first mindset and leveraging automated security tools can significantly reduce the risk of breaches. Continuous vulnerability assessments and integrating security into the development lifecycle are also crucial components of a strong cloud security posture.
Work in Government? Learn all you need to know from our cloud experts about which government cloud offering will work best for you: GovCloud and Azure Government.
The Cloud Optimization Process
Cloud optimization efforts typically go through the following stages.
1. Identify Workloads
The first step in cloud optimization is identifying and categorizing your workloads. This involves analyzing all applications, services, and processes in your cloud environment to understand their resource requirements, operational behavior, and usage patterns. Group workloads based on compute needs, storage demands, data transfer volumes, and peak usage times. Organizations can tailor optimization strategies by classifying workloads to meet specific requirements, making allocating the right amount and type of resources more accessible.
For instance, workloads that experience heavy traffic periodically may benefit from auto-scaling, while stable workloads might be more cost-efficient on reserved instances. Understanding workload profiles is essential to avoiding both over- and under-provisioning, ensuring that resources are aligned with actual usage.
2. Select Appropriate Resources
Once workloads are identified, the next step is choosing the most suitable cloud resources. This includes selecting the correct instance types, storage solutions, and networking options based on workload needs. Right-sizing resources is crucial—choosing too large an instance or storage volume can result in wasted spend, while undersized resources can lead to performance issues.
Different cloud providers offer a range of options for compute, memory, and storage configurations. For example, general-purpose instances are often ideal for balanced workloads, while compute-optimized or memory-optimized instances may be better suited for high-performance tasks. Selecting the right mix ensures that resources are cost-effective and can support application performance requirements.
3. Monitor Usage
Continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining an optimized cloud environment. By tracking resource usage over time, organizations can identify trends, spot inefficiencies, and adjust resources as needed. Monitoring tools provide visibility into metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, storage I/O, and network bandwidth, allowing teams to pinpoint underutilized or idle resources.
Cloud providers often offer native monitoring solutions; third-party tools can provide additional insights and integrations. Setting up alerts and dashboards to monitor key performance indicators enables proactive adjustments, helping prevent resource waste and maintain cost efficiency. Effective monitoring supports capacity planning and helps anticipate scaling needs based on historical usage data.
4. Optimize
Optimization involves applying changes based on insights gained from monitoring. This could mean rightsizing instances, implementing cost-saving strategies like spot instances, and automating scaling processes to adjust resources according to demand dynamically. Optimization can include implementing caching strategies, refining load balancing configurations, and utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to improve application response times.
Reviewing and refining resource configurations helps ensure the cloud environment remains efficient as workloads evolve. Optimization should be a continuous cycle, where organizations periodically reassess and adjust their cloud environment to align with changing business needs, demand fluctuations, and technological advancements.

David Drai
CEO & Co-Founder, Anodot
David is dedicated to helping companies uncover business insights with AI analytics, backed by a strong background in leading tech innovations.
TIPS FROM THE EXPERT
1. Leverage spot instances and reserved instances
Use spot instances for flexible workloads that can handle interruptions, and reserved instances for predictable, steady workloads. These strategies significantly reduce costs by allowing you to access cloud resources at discounted rates while optimizing performance for various types of applications.
2. Automate anomaly detection and response
Set up automated tools that detect anomalies in resource usage, such as sudden cost spikes or performance bottlenecks. These tools can notify your teams when something unusual occurs, allowing for a quick response and preventing inefficiencies or costly misconfigurations.
3. Utilize performance optimization techniques
Optimize application performance by utilizing caching, load balancing, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). Additionally, ensure databases are properly indexed, and data is structured efficiently. These tactics reduce latency, improve load times, and enhance the user experience.
4. Automate scaling and resource provisioning
Take advantage of cloud auto-scaling features to dynamically adjust your resource allocation in response to real-time demand. This helps prevent under-provisioning during peak times and avoids over-provisioning during off-peak hours, maintaining cost-efficiency and performance.
5. Track multicloud costs and optimize accordingly
If your organization uses multiple cloud providers, employ multicloud cost management tools to track spending across platforms. These tools help you optimize resource allocation, avoid redundant services, and take advantage of cost-saving opportunities specific to each cloud provider.”
Types of Cloud Optimization Services and Tools
1. Multicloud Cost Management Tools
Multicloud cost management tools provide visibility and control over spending across multiple cloud platforms. These tools aggregate cost data, provide comprehensive analytics, and recommend cost-saving measures.
Using multicloud cost management tools, organizations can identify unnecessary expenditures, optimize resource allocations, and take advantage of the best pricing options available across different cloud providers. This holistic approach to cost management is crucial for businesses leveraging services from multiple cloud vendors, ensuring that their cloud strategy is cost-effective and efficient.
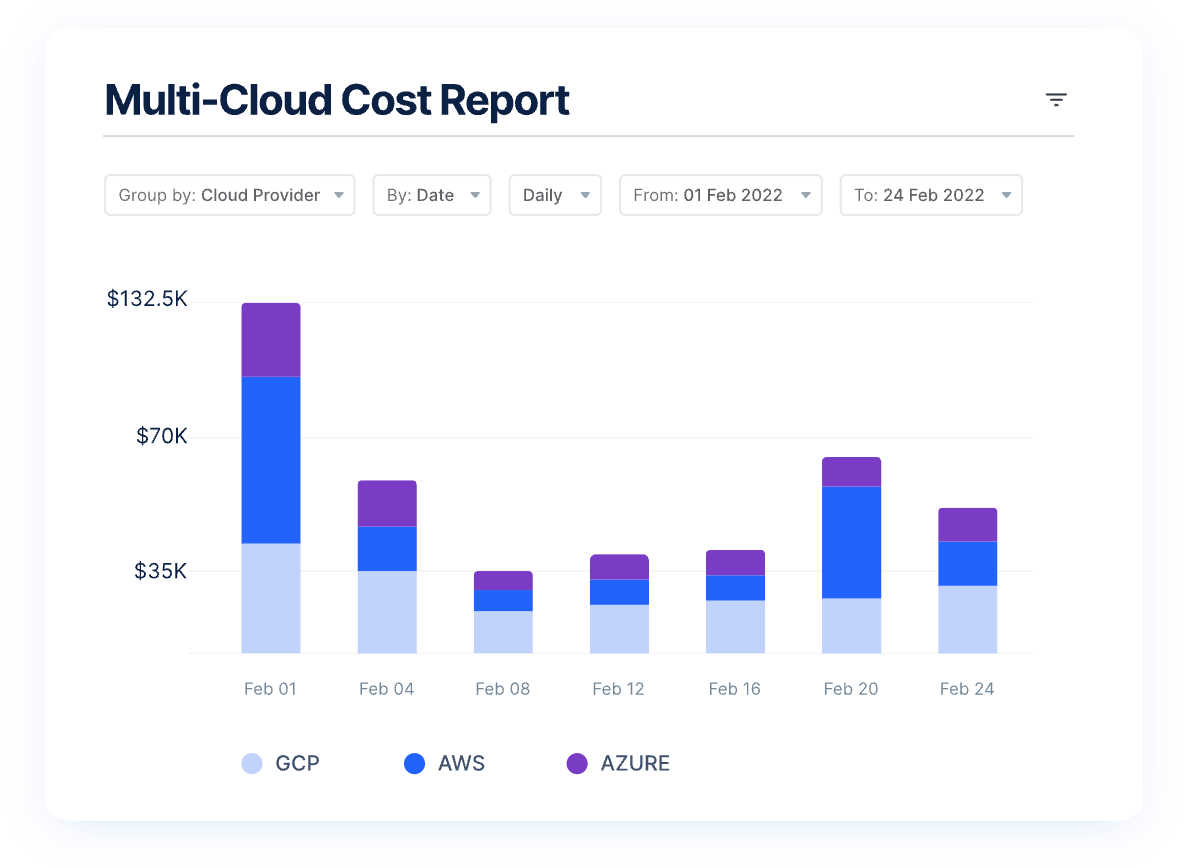
2. Kubernetes Cost Optimization
Kubernetes cost optimization focuses on managing and reducing the costs of running containers in Kubernetes environments. Tools and strategies for Kubernetes cost optimization include rightsizing container resources, implementing efficient cluster autoscaling, and using spot instances for non-critical workloads.
By monitoring and optimizing Kubernetes resources, organizations can significantly reduce the overheads associated with container orchestration, ensuring that their containerized applications run efficiently without overspending on infrastructure.
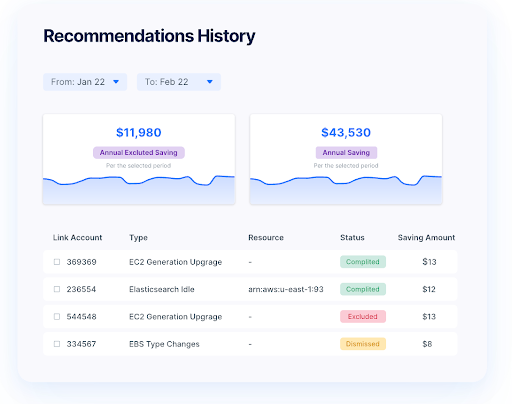
3. Performance Optimization Tools
Performance optimization tools focus on monitoring and improving the speed and responsiveness of applications in the cloud. These tools analyze application performance, identify bottlenecks, and provide recommendations for enhancements. Organizations can use performance optimization tools to ensure their applications meet user expectations and perform efficiently under varying load conditions.
These tools also help in capacity planning, enabling businesses to scale resources up or down based on real-time demand. This dynamic approach to resource management ensures optimal performance while avoiding unnecessary costs.
4. Storage Optimization Services
Storage optimization services are designed to help organizations manage their data storage needs more efficiently. These services offer features like data deduplication, compression, and tiering, which can significantly reduce storage costs and improve access speeds. By optimizing storage, businesses can ensure that data is stored cost-effectively without compromising accessibility or security.
Moreover, storage optimization services facilitate better data management practices, such as archiving old data to cheaper storage options and automatically moving frequently accessed data to higher-performance storage. This not only reduces costs but also improves data access performance.
5. Cloud Security Solutions
Cloud security solutions focus on protecting cloud environments from internal and external threats. These solutions offer a range of features, including identity and access management, threat detection, data encryption, and security compliance.
By deploying cloud security tools, organizations can strengthen their defense against cyberattacks, prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information, and ensure their cloud deployments comply with industry regulations and standards. Additionally, these tools can automate security processes, making it easier to manage security at scale.
Challenges in Cloud Optimization
Complex Pricing Models
One of the major challenges in cloud optimization is navigating the complex pricing models cloud providers offer. Cloud platforms often have intricate pricing structures that vary based on resource type, region, usage level, data transfer volumes, and even time of day. Cloud providers offer multiple pricing options—on-demand, reserved, and spot instances—each with different pricing and commitment requirements.
Without clear insight into pricing, organizations may inadvertently overspend by selecting suboptimal pricing plans or failing to take advantage of available discounts. Effective optimization, therefore, requires a deep understanding of the provider’s pricing model and tools that can analyze costs across different configurations, regions, and service levels.
Resource Sprawl
Resource sprawl occurs when cloud resources proliferate uncontrollably due to decentralized management, lack of oversight, or inadequate tracking. In cloud environments, creating new resources is easy, but this can lead to redundant, unused, or oversized resources accumulating over time. This issue is widespread in environments where multiple teams or departments have the authority to provision their cloud resources without centralized monitoring.
Resource sprawl leads to inefficiency and increased costs. As organizations end up paying for resources they may not fully utilize. Addressing this challenge requires implementing policies for resource tagging, regular audits, and automated tools to identify and clean up idle or underutilized resources. Governance practices such as setting quotas or requiring approval for new resources can also help reduce sprawl.
Skill Gaps
Cloud optimization often demands specialized skills and a strong understanding of cloud architecture, cost management, and performance tuning. However, many organizations face skill gaps as their teams may lack experience with cloud-specific tools and optimization practices. The rapid evolution of cloud technologies compoundes this challenge, making it difficult for teams to stay current on best practices and new optimization tools.
To bridge skill gaps, organizations may need to invest in targeted training and certification programs or hire cloud specialists with expertise in cost management, scaling, and cloud-native development. Additionally, adopting managed services or partnering with cloud consulting firms can provide access to expertise while allowing internal teams to build their own skill sets gradually.
Best Practices to Optimize Your Cloud Environment
1. Right Sizing Cloud Resources
Right sizing involves adjusting the size and capacity of cloud resources to match the demand closely. Many organizations overprovision resources to avoid performance issues, leading to unnecessary costs. Rightsizing ensures that each resource is the appropriate size for its workload, maximizing cost-efficiency without compromising performance.
This process should be continuous, as workloads and application demands can change over time. It is important to routinely review and adjust resources, maintaining an optimal balance between performance and cost.
2. Address Anomalies
Identifying and addressing anomalies in cloud usage is vital for maintaining an optimized environment. Anomalies, such as sudden spikes in resource usage or unexplained cost increases, can indicate inefficiencies or misconfigurations. Monitoring tools and services can help detect these irregularities early, allowing for prompt investigation and resolution.
Organizations can proactively address anomalies and reduce wasteful spending by avoiding potential performance issues. This process involves regular audits of cloud resources and usage patterns, ensuring that resources are being utilized most effectively.
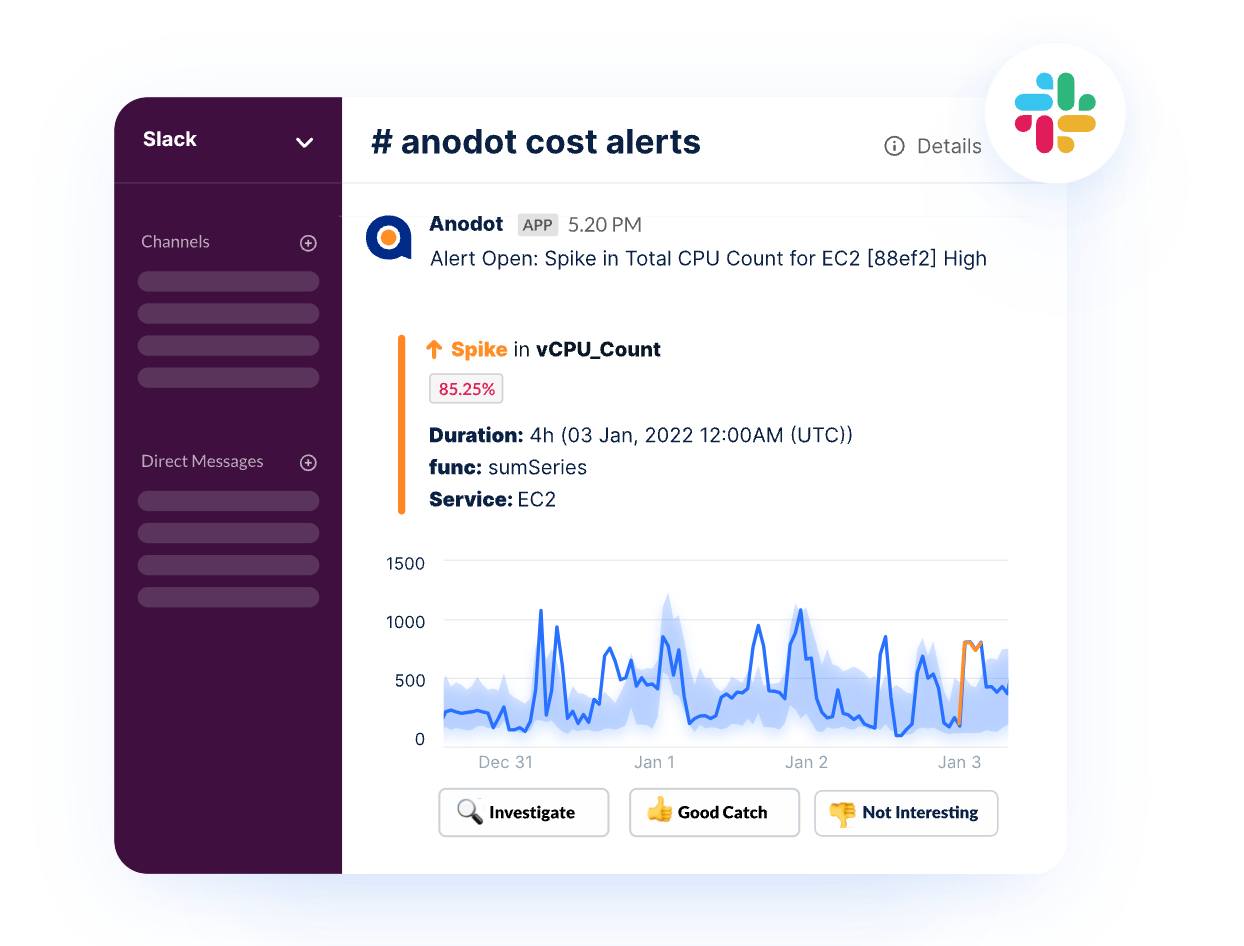
3. Making Use of Spot and Reserved Instances
Leveraging spot and reserved instances can significantly reduce cloud computing costs. Spot instances allow users to bid for unused cloud capacity at lower prices, ideal for flexible, non-critical workloads. Reserved instances offer discounted rates for a commitment to use a specific resource over a predetermined period.
Both options require careful planning and management to maximize savings while meeting workload requirements. Understanding your application’s tolerance for interruptions and long-term resource needs is key to making the most of these pricing models.
4. Use Automated Tools to Streamline and Automate Optimization Tasks
Automated tools play a critical role in optimizing cloud environments. They can automate routine tasks such as resource provisioning, scaling, and monitoring, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human error. This saves time and ensures a more consistent and efficient operation of cloud resources.
Advanced cost optimization tools can also help implement cost-saving measures, such as shutting down idle resources, scaling services based on demand, and applying spot or reserved instances for relevant workloads. Integrating these tools into your cloud strategy can save time and generate more significant cost savings and performance improvements.
5. Using Managed Service Providers (MSPs) for Cost Optimization
Managed service providers (MSPs) offer a way to optimize cloud environments further. These services can include database management, application monitoring, and security. By leveraging the expertise of managed service providers, organizations can improve efficiency, enhance security, and reduce the burden on internal teams.
Additionally, managed services can help optimize costs by providing access to advanced tools and resources without significant upfront investment. This allows organizations to benefit from high-quality services while focusing on core business functions.
6. Utilizing AI for Cost Optimization
AI is becoming increasingly important for cloud cost optimization. These tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict future usage trends, and recommend actions to reduce costs. For instance, AI can suggest the best times to purchase reserved instances or identify underutilized resources that can be downsized.
By leveraging AI for cloud optimization, organizations can take a proactive approach to managing their cloud expenses. These tools provide valuable insights that can lead to more informed decision-making and ultimately, a more cost-efficient cloud environment.
Cloud Optimization with Anodot
Anodot can significantly aid companies in cloud management in the following ways:
- Real-time Anomaly Detection: Anodot’s platform swiftly identifies unusual cloud cost spikes, enabling proactive cost management and prevention of overruns.
- Automated Insights: Leveraging AI provides actionable insights for efficient cloud resource utilization and cost reduction strategies.
- Multi-cloud Support: Anodot handles environments spanning multiple cloud platforms, offering unified visibility and control.
- Customizable Alerts: Tailored alerting systems inform teams of critical changes or issues in cloud usage and expenditure.
- Advanced Forecasting: The platform offers predictive analysis for future cloud spending, aiding in better budgeting and financial planning.
These capabilities make Anodot a valuable tool for companies looking to optimize their cloud infrastructure and finances effectively.






