Network Address Translation Gateway or NAT Gateway is a managed service provided by Amazon Web Services(AWS) that allows instances in a private Subnet within a Virtual Private Cloud(VPC) to connect services outside the VPC.
NAT ensures that even though your instances can connect to the outside world, outside services can’t establish a direct connection with them. It’s a tool that secures the instances, simplifies network architecture, and reduces administrative overhead.
What are the connectivity types of NAT Gateway?
There are two connectivity types of NAT Gateways:
Public NAT Gateway: This is the most common type. It allows instances in a private subnet to connect to the Internet but cannot receive unsolicited inbound connections from the Internet.
Private or NAT Gateway for VPC Peering: This type of NAT Gateway facilitates communication between resources in your VPC and resources in a peered VPC that does not have a public internet gateway.
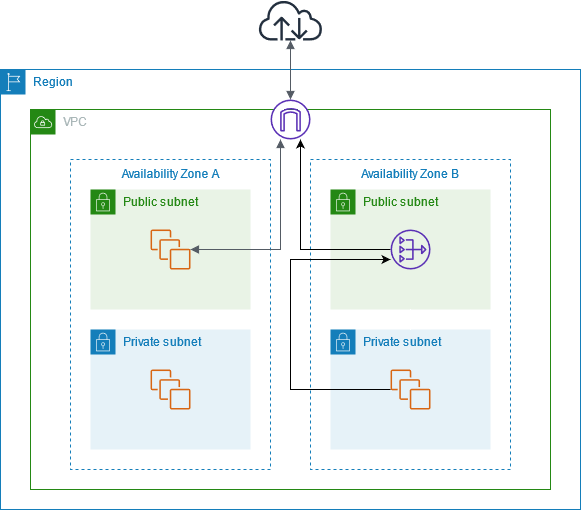
NAT Gateway works as follows:
- In a typical cloud setup, you have public and private subnets within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Instances in the private subnet don’t have direct internet connectivity.
- When an instance in the private subnet needs to access the internet (e.g., to download updates, connect to external APIs, or retrieve data), it sends the outbound traffic to the NAT Gateway.
- The NAT Gateway translates the private IP addresses of the instances in the private subnet to its public IP address. This means that internet resources see the traffic coming from the NAT Gateway’s public IP address rather than the private IP addresses of the instances.
- After the translation, the NAT Gateway forwards the traffic to the internet.
- When the internet resources respond to the outbound traffic, they send the responses back to the NAT Gateway.
- The NAT Gateway receives the responses, translates the destination IP address back to the private IP address of the originating instance, and forwards the response to the instance in the private subnet.
Costs Associated with NAT Gateways
NAT Gateway incurs two types of costs:
Usage Costs(Hourly Charge): You are charged per hour that a NAT Gateway is provisioned and available in your VPC, regardless of whether it’s actively processing traffic. The price varies depending on the AWS region of your NAT Gateway.
Data Processing Charge: You are charged for every Gigabyte (GB) of data that passes through the NAT Gateway. This includes outbound traffic from your private instances to the internet and any return traffic generated in response to those outbound requests.
What are the benefits of NAT Gateway?
The benefits of NAT Gateway are as follows:
Public Internet Access: NAT Gateway allows resources within private subnets to access the Internet for tasks such as downloading updates, accessing external APIs, or fetching data without exposing their private IP addresses to the Internet.
Improved Security: NAT Gateways allow you to keep your instances in private subnets within your VPC anonymous. This isolates them from the public Internet, significantly reducing the attack surface for malicious actors. Only authorized outbound traffic can flow through the NAT Gateway, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to your resources.
Simplified Management: NAT Gateways eliminate the need to provision, configure, and maintain your own NAT instances. This simplifies your network architecture and reduces your administrative overhead. AWS manages the underlying infrastructure and ensures its availability and scalability.
Scalability: NAT Gateways can automatically scale up or down based on your instances’ outbound traffic demands. This ensures that your NAT Gateway can handle traffic spikes without performance degradation. You don’t need to adjust resources to meet changing demands manually.
Cost-Efficiency: While there are costs associated with NAT Gateways (hourly rate and data processing), they can sometimes lead to cost savings compared to alternative solutions. For example, if your instances only require outbound connections to specific AWS services, NAT Gateways might be more cost-effective than using individual Elastic IP addresses for each instance.
High Availability: AWS NAT Gateway is designed to be highly available, with built-in redundancy across multiple availability zones (AZs). This ensures that your outbound internet traffic remains uninterrupted even in a failure in one availability zone.
Monitoring and Logging: AWS provides monitoring and logging features for NAT Gateways, allowing users to track outbound traffic patterns, monitor usage, and troubleshoot connectivity issues effectively. This visibility helps in optimizing resource usage and identifying potential security threats.
FinOps for NAT Gateways
FinOps is an operating model that brings financial accountability to variable spending in the cloud. It ensures that cloud costs are aligned with a company’s business objectives. Implementing FinOps principles can help optimize costs associated with using NAT Gateways. With Anodot, FinOps teams can easily classify and divide all their cloud costs by business structures like apps, teams, and lines of business using business mappings.
Anodot helps identify and allocate the shared costs of different business departments in a company. Its business mappings help split the shared-costs across different departments using FinOps models. Such as:
- Even split: the targeted costs are split evenly among all departments.
- By percentage: the targeted costs are split by custom percentages.
- Proportional: the targeted costs are divided based on the relative percentage of direct costs.
Anodot empowers FinOps teams to:
- Boost engineering trust in NAT Gateway spending by providing clear data and insights.
- Pinpoint, which gateway is acting as a cost center.
- Track overall cloud costs across different business areas over time.
- Find unallocated gateway costs to optimize budgeting.
- Simplify cost allocation for clear accountability (showback) and cost recovery (chargeback).
- Make strategic investments based on accurate data.
How to Optimize NAT Gateway Cloud Costs using Anodot?
Anodot Cloud Cost is a valuable tool for identifying and reducing idle resource problems associated with your AWS NAT Gateways, ultimately optimizing your cloud spending. Anodot can be leveraged in the following ways to optimize NAT Gateway costs:
Identifying Idle NAT Gateways: Anodot leverages machine-learning algorithms to analyze your NAT Gateway usage patterns. It can identify provisioned NAT Gateways but not actively process significant outbound traffic. These instances are idle and accumulate usage costs but not data processing costs. Such instances can be terminated if found redundant.
Visualization and Alerting: Anodot provides insightful dashboards and visualizations that display your NAT Gateway usage metrics over time. You can easily see which NAT Gateways are experiencing low traffic and potentially incurring unnecessary costs.
Anodot can also be configured to send alerts when a NAT Gateway exhibits a sudden drop in traffic or falls below a predefined utilization threshold. This allows you to take proactive action and optimize resource allocation.
Recommendations and Insights: Anodot uses ML analysis to provide tailored recommendations for optimizing your NAT Gateway usage. For example:
- Right-sizing your NAT Gateways: If you’re using a larger NAT Gateway than necessary for your traffic volume, Anodot might recommend downsizing to a smaller, more cost-effective option.
- Scheduling on/off times: If your application has predictable usage patterns with off-peak hours, Anodot could recommend automating the creation and deletion of NAT Gateways during those times. This allows you to pay only for the time you need the resource.
- Exploring alternative solutions: Anodot might identify situations where alternative solutions like VPC endpoints could be more cost-effective for specific outbound traffic needs.
How does Anodot allocate NAT Gateway costs?
The majority of the cost management tools provide filtering and grouping capabilities that combine multiple filters and tags into a category and use that as the basis for cost allocation, this results in overlapping costs, which leads to inaccurate reporting. To tackle this issue, Anodot provides the capability of business mapping that empowers you to:
- Accurately map spending data to relevant business dimensions without overlap
- Assign shared costs equitably
- Report cloud spend in a way that is customized to your organization’s needs
Anodot allows you to allocate NAT Gateway costs to specific departments, projects, or applications within your organization. This cost allocation helps you track spending more granularly and identify areas for potential cost optimization across your cloud infrastructure.
Anodot’s cost allocation tools provide comprehensive reports that detail your NAT Gateway usage and related costs. These reports can be used to monitor your progress in cost optimization efforts and make informed decisions for future resource allocation.
Book your Demo today!
See how Anodot delivers FinOps visibility and deep savings across multi-cloud and K8s





