Amazon EC2 Explained
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is one of the core services of AWS, designed to help users reduce the cost of acquiring and reserving hardware.
EC2 represents the compute infrastructure of Amazon’s cloud service offerings, providing organizations a customizable selection of processors, storage, networking, operating systems, and purchasing models.
It is known for assisting organizations to simplify and speed up their deployments for less cost and enabling them to increase or decrease capacity as requirements change quickly.
However, the costs associated with instances and features in EC2 can soon get out of control if not properly managed and optimized. The first cost consideration is usually selecting an instance type.
EC2 Instance Types
Even for experienced cloud engineers and FinOps practitioners, EC2 pricing is extraordinarily complex. Many options impact cost, with instances optimized for workload categories like compute, memory, accelerated computing, and storage.
The default option for purchasing is on-demand instances, which bills based on seconds or hours of usage but require no long-term commitments. EC2 instances are grouped together into families. Each EC2 family is designed to meet a target application profile in one of these buckets:
General Purpose Instances
General-purpose instances provide a balance of computing power, memory, and networking resources and can be used for everyday workloads like web servers and code repositories.
Compute Optimized
Compute-optimized instances are best suited for applications that benefit from high-performance processors.
Memory-Optimized
Memory-Optimized instances deliver faster performance for workloads that process large data sets in memory.
Accelerated Computing
Accelerated Computing instances leverage hardware acceleration and co-processors to perform complex calculations and graphics processing tasks.
Storage Optimized
Storage optimized instances are designed for workloads requiring high performance, sequential read and write access to large-scale datasets.
When considering the cost, each instance type above can vary by region or operating system selections.
The Hidden Cost of EC2
While AWS documents the cost of each instance type by region in their EC2 Pricing, getting to the actual price of using these services requires much more consideration. The first thing to consider is the status of the EC2 instance. Customers pay for computing time, disk space, and data traffic if in a running state.
Customers may still incur charges for unattached IPs and any active (not deleted) storage when in a stopped state. Unfortunately, many users mistakenly believe that stopping their servers will stop further costs from accruing, and this is not the case.
Another potential hidden cost of using EC2 is data traffic. AWS calculates data traffic costs by tier, based on a pre-defined volume with traffic falling below the volume incurring less cost and anything above paying more.
Because AWS charges for data traffic at the account level, many manual monitoring processes fall short in projecting actual costs. Considering how many AWS services comprise the AWS account of a large-scale program or company, it’s easy to imagine how difficult it would be to monitor and control cloud spending in AWS.
How to reduce AWS EC2 Spending
Here are some of the best practices to reduce EC2 spending in AWS:
EC2 Right-Sizing
Many developers fail to consider right-sizing when spinning up AWS resources, but it’s a critical component of optimizing AWS costs. AWS also defaults to many flexible but pricey options like On-Demand instances. Choosing a suitable instance type and service tier can significantly reduce cost without impacting performance.
EC2 Generation Upgrade
AWS offers different instances tuned specifically for various workloads, as discussed above. When selecting an instance type, look for the latest generation options because they often provide the best performance and pricing.
Unnecessary Data Transfers
AWS charges for inter-Availability Zone data transfer between EC2 instances even if they are located in the same region. Whenever possible, co-locate all instances within a single Availability Zone to avoid unnecessary data transfer charges.
Stopped Instances
Stopping EC2 instances does not eliminate the potential for charges. Resources attached to stopped instances like EBS volumes, S3 storage, and public IPs continue to accrue costs. Consider terminating attached resources or the instance if it is no longer in use.
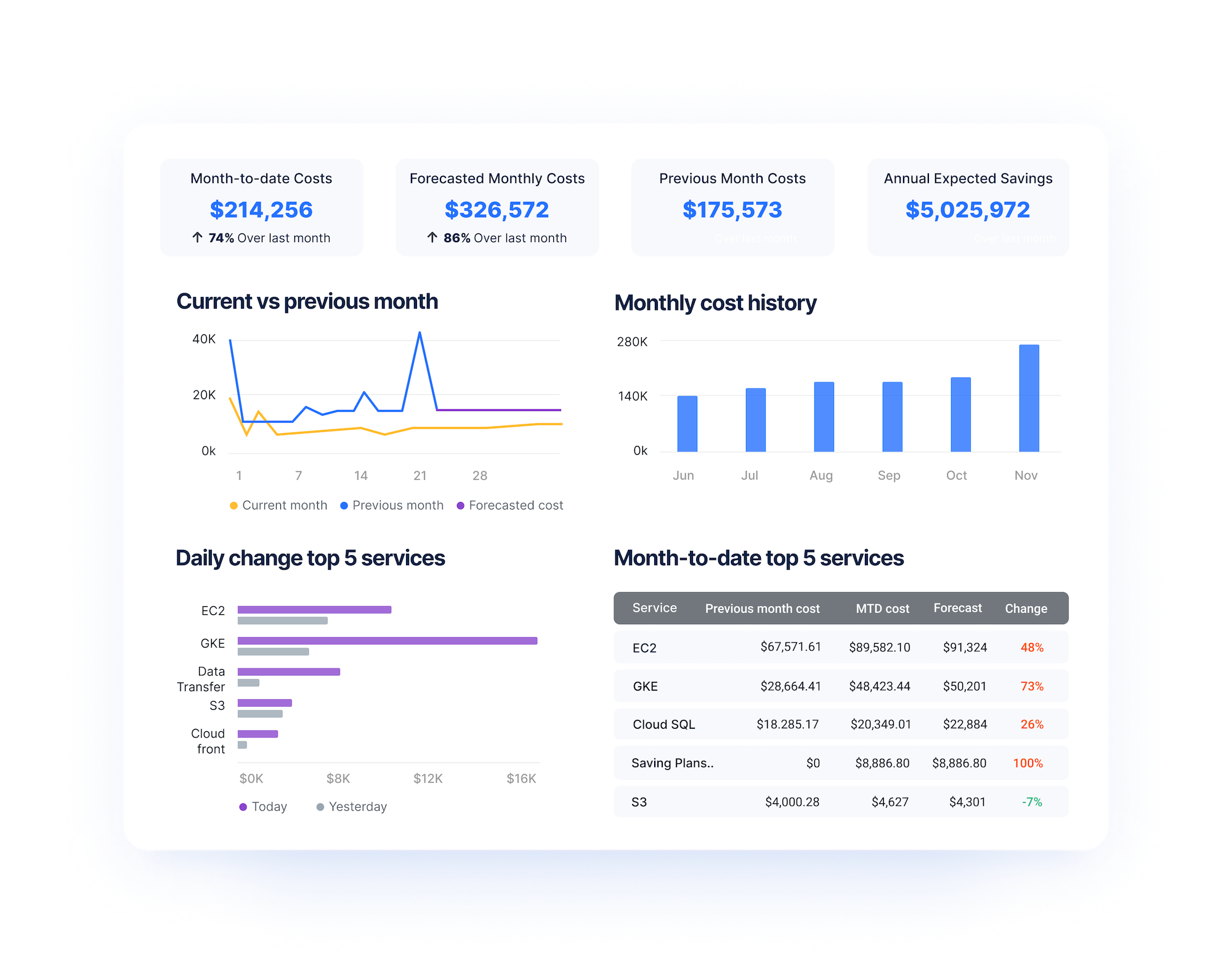
Optimize EC2 Cost with Anodot
Anodot’s Cloud Cost Management solution makes optimization easy. It can easily connect to AWS, Azure and GCP to monitor and manage your spending. Even with multi-cloud environments, Anodot seamlessly combines all cloud spending into a single platform allowing for a holistic approach to optimization measures.
What makes Anodot for Cloud unique is how it learns each service usage pattern, considering essential factors like seasonality to establish a baseline of expected behavior. That allows it to identify irregular cloud spend and usage anomalies in real-time, providing contextualized alerts to relevant teams so they can resolve issues immediately.
Proprietary ML-based algorithms offer deep root cause analysis and clear guidance on the steps for remediation. Customers are already using Anodot to align FinOps, DevOps, and finance teams’ efforts to optimize cloud spending.
Accurate forecasting is one of the central pillars of FinOps and cloud cost optimization. Anodot leverages AI-powered forecasting with deep learning to automatically optimize cloud cost forecasts and enable businesses to react to changing conditions before impacting cost.
Rather than manually watching cloud resources and billing, your analysis teams will view cloud metrics with a business context in the same place as revenue and business metrics. That allows FinOps practitioners to optimize cloud investments to drive strategic business initiatives continually.
Start Reducing Cloud Costs Today!
Connect with one of our cloud cost management specialists to learn how Anodot can help your organization control costs, optimize resources and reduce cloud waste.